Disc Couplings
Disc couplings are high-performance, torsionally rigid couplings designed for precise torque transmission without backlash. They use flexible metallic disc packs to accommodate angular and axial misalignment while maintaining high torsional stiffness.
They are ideal for high-speed and high-precision applications such as pumps, compressors, turbines, and process equipment.
Key Benefits:
Zero backlash
High torsional rigidity
No lubrication required
Excellent performance at high speeds
Long service life
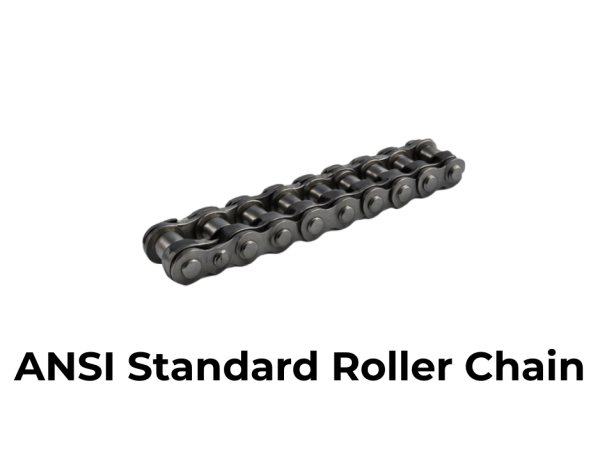
Chain Couplings
Chain couplings consist of two sprockets connected by a double-strand roller chain. They are simple, durable, and capable of handling high torque loads while allowing moderate misalignment.
Commonly used in heavy industrial machinery, conveyors, mixers, and general power transmission systems.
Key Benefits:
High torque capacity
Easy installation and maintenance
Cost-effective solution
Suitable for harsh environments
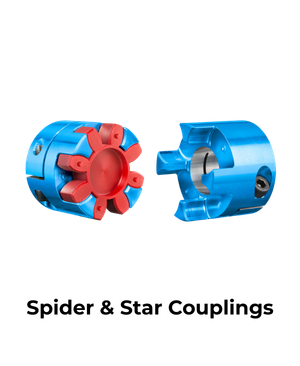
Spider & Star Couplings
Spider (jaw) and star couplings use two metal hubs and an elastomeric insert (spider/star) to transmit torque while absorbing vibration and shock loads.
They are widely used in pumps, motors, compressors, and general industrial applications where damping and flexibility are required.
Key Benefits:
Excellent vibration damping
Shock load absorption
Maintenance-friendly design
No lubrication required
Available in different elastomer hardness options
Gear Couplings
Gear couplings are designed for high torque transmission in demanding applications. They consist of two hubs with external gear teeth and a sleeve with internal teeth, allowing torque transmission while accommodating misalignment.
They are commonly used in steel mills, mining equipment, heavy-duty conveyors, and high-power industrial systems.
Key Benefits:
Very high torque capacity
Compact design for transmitted power
Accommodates angular and parallel misalignment
Suitable for heavy-duty applications